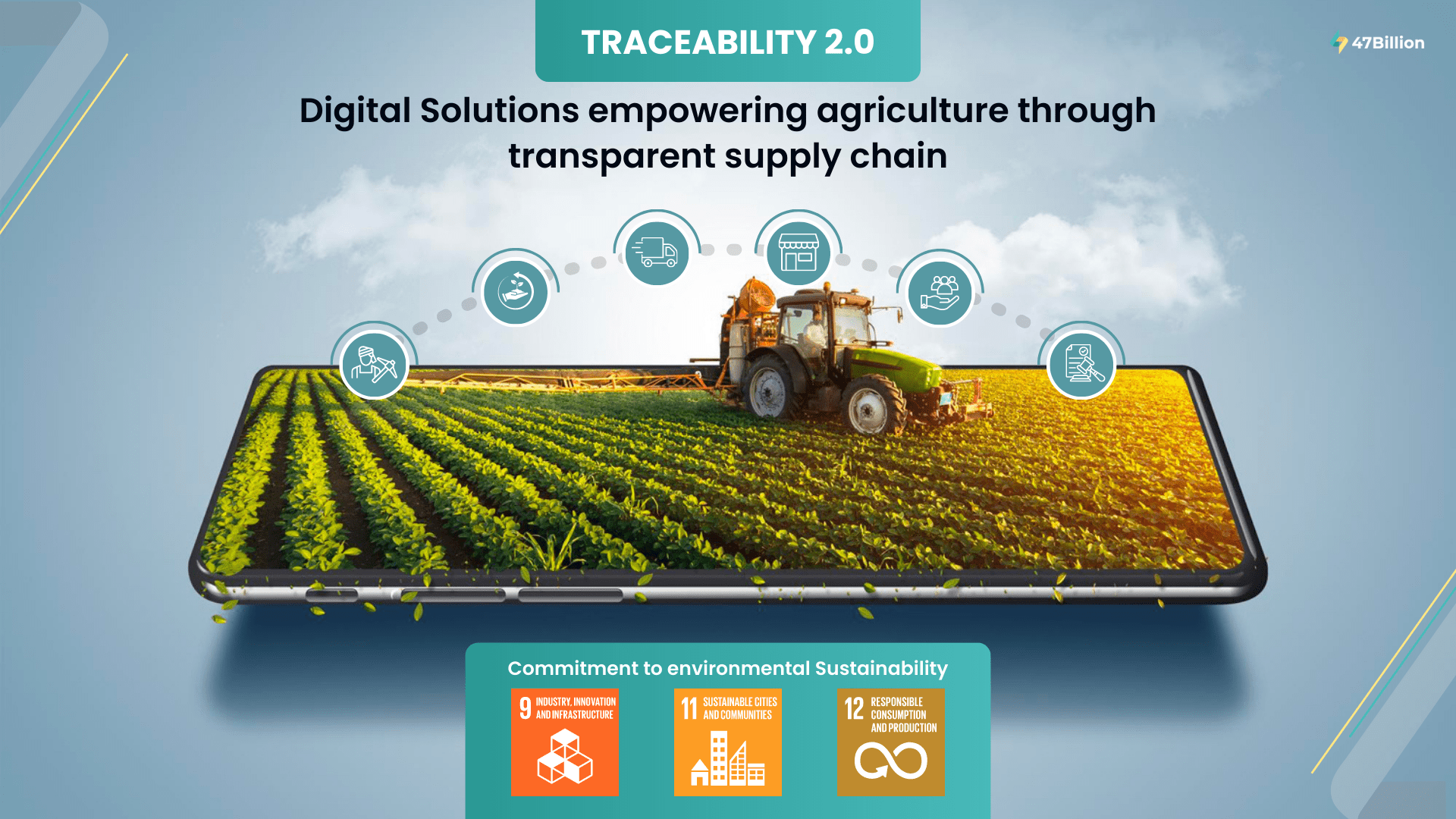
Transparency is the key to business success- this has become increasingly apparent in the agriculture industry. Are you aware that the past pandemic has shed light on the central issue for the Australian agriculture industry, “traceability”? Over the past year, the shift in imports and exports has increased Aussies’ demand for improved visibility over where their food originates and how it is grown. Also, Australian farmers want assurance that their product is handled well and remains top-quality during its journey to local retailers or overseas markets.
Today this has become a global challenge. Improving Traceability across the board could fix it. Specially designed traceability systems can help farmers and all the agriculture industry stakeholders track their products along the supply chain, eliminating potential bottlenecks and improving the ecosystem.
On the other hand, consumers can take advantage of the technology by tracking their produce back from the original source, enabling more conscious consumption and trust while purchasing.
What is Traceability?
Traceability is the ability to share information about the movement of an agricultural product and follow through all the stages of the supply chain, that is, from production to processing and distribution. It is defined by the purpose and user requirements for specific data at a point in the supply chain.
Effective Traceability can provide exact information about a product’s journey from farm to end consumer.
Key drivers of Traceability – Why is it crucial?

Globally, the importance of improved Traceability is driven by –
Compliance & Regulation
- Food Safety – Regulations help protect consumers and ensure correct production processes, controls, and accreditations.
- Biosecurity – The compliance and regulation practices are in place to minimize the risk of transmission to people, animals, and plants.
- Market Access – These regulations and compliance include official trade restrictions for importing countries in addition to their food safety and biosecurity measures.
Building & Establishing Brands
- Awareness of Origin – digital Traceability can help quickly confirm where particular food was produced and manufactured and how it was transported, eliminating food fraud.
- Certifications – Certifications and product attributes refer to a quality or feature consumers value, such as organic, fair trade, and sustainable.
Improving Production Efficiencies
- Supply Chain Efficiency & Quality – An efficient global supply chain can reduce costs, increase speed to market, support volume and safeguard the quality of goods; particular perishable produce helps in improved forecasting.
What is a traceability system?
Traceability systems help firms manage the flow of inputs and products to improve efficiency, product differentiation, food safety, and product quality. Firms balance the private costs and benefits of Traceability to determine the efficiency level. In cases of market failure, when the private sector supply of Traceability is not socially optimal, the private sector gets several mechanisms to correct the situation, including contracting, third-party safety/quality audits, and industry-maintained standards. It includes the best-targeted government policies that strengthen firms’ incentives to invest in Traceability, aiming at ensuring that unsafe or falsely advertised foods that can be quickly eradicated from the system. It also has policy review tools, including timely recall standards, increased penalties for distributing unsafe foods, and improved foodborne-illness surveillance.
Digital Framework
Amongst all the evolving systems developed around this concept, a web application is in the process of development that facilitates crop traceability. The application is intended to help farmers, producers, buyers, and consumers trace the movement of Agri products from farm to market.
The web app is an easy-to-use interface that allows users to produce digital records of crops, including information regarding variety, location, and production practices. This data is then securely kept and is accessible to authorized parties across the supply chain.
Moreover, it allows farmers and producers to connect with buyers and gain access to new markets. This expands market access and economic prospects for smallholder farmers and cooperatives. The online application provides an integrated approach for increasing transparency and sustainability in the agricultural business, addressing supply chain difficulties, and boosting market access for smallholder farmers and microentrepreneurs.
The system consists of 4 major user roles -
Super Admin: Super admin can inspect and modify the status of all registered cooperatives, cooperative-related farmers, and registered items.
Cooperative: The cooperative can use this panel to add new farmers, update a farmer’s active status, create a crop request for the farmer, and place client orders.
Farmer: A farmer can register crops here in response to requests made by the attached cooperative or plant his own.
Earth User: The user who can witness the system.
How is it transforming the scenario?
The web application has the following features –
- Tracking the records of crops, farmers, and cooperatives to maintain inventory based on tracks.
- Smooth and transparent collaboration channels for cooperatives and farmers.
- Cooperatives can deal with and request orders of crops from farmers and take orders for clients with order traceability. The data generated is used for further research and analysis in agriculture.
- Sustained productivity with good management practices.
- Helping farmers to grow crops suitable to local and regional climate and crop management needs
- Cooperatives can communicate about any trend relevant to the crop, especially in case of any disease that may need attention from farmers, so this timely information may help farmers take necessary measures.
- Also, cooperatives can educate farmers about standard or region-specific practices related to crops for optimum production.
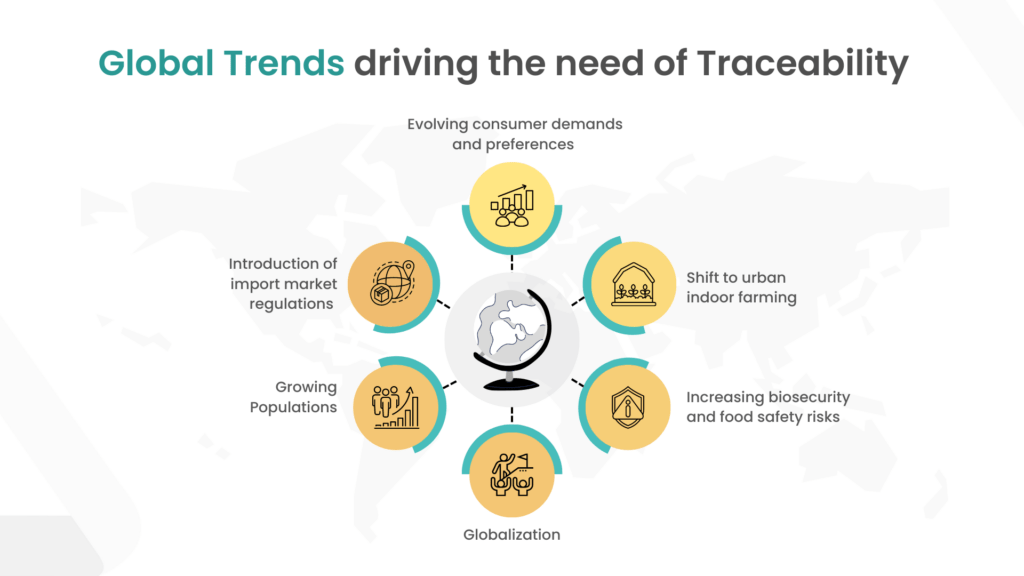
Global Trends Driving the Need of Traceability
Towards a Sustainable Future
The global food supply chain is becoming a complicated process as firms attempt to improve their skills to feed the world’s rising population. While food safety issues are becoming a challenge thus, it is essential to understand every stage of the supply chain. Traceability systems thus help businesses execute methods for tracking and tracing items’ journeys throughout the supply chain to improve food safety and security. They ensure that the crops are grown and marketed responsibly and sustainably using digital record-keeping. This can include tracking pesticide and fertilizer use, monitoring water usage, and promoting environmentally friendly farming practices like agroforestry and intercropping.
47Billion is glad to announce an enhanced business strategy formulated to maximize the combined impact of its technologies, solutions, and capabilities to address some of the biggest global challenges and support the UN Sustainability Development Goals.
Read related articles –
- 47Billion Is Taking UN Sustainability Goals To The Next Level Of Impact
- Vertical Farming: Harnessing Technology For Sustainable Agriculture
- Water Trading: Paving The Way For Sustainable Conservation In California’s Drought Zones